There is no denying that the olfactory nerves of dogs and cats are more sensitive than those of other animals. In fact, these animals can smell prey from far away.
But if you compare a dog nose vs cat nose, which furry pet can detect scents better?
This article will discuss the differences between a dog vs cat sense of smell. We’ll also compare the animals’ other senses, so make sure to stick with us till the end.
Table of Contents
Cat and Dog Sense of Smell: Overview
While dogs and cats utilize their sense of smell to explore their environments, the latter use vomeronasal receptors more than dogs do. In other words, they rely more on chemical signals and less on smells to find food.
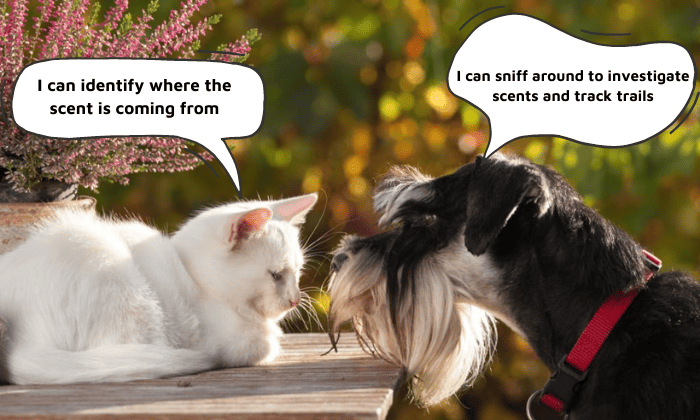
Dogs are popular for their pronounced sniffing. They actively sniff around to investigate scents and track trails.
These animals also use their noses to gather the scent of the things they find new or interesting.
Do cats sniff like dogs? The quick answer is no.
Cats have an olfactory organ called the Jacobson’s organ, which is located in the roof of their mouths.
When cats smell things, they perform the Flehmen response. To do this, they open their mouth slightly and curl back their upper lips to expose the Jacobson’s organ.
This way, they can gather chemical signals from the scent, allowing them to identify what it is and where it is coming from.
Although dogs have the same Jacobson organ in the nasal cavity and mouth, they only possess eight genes relating to vomeronasal scenting, while cats have twenty-one.
Cat vs Dog Sense of Smell: Comparing the Differences
1. Number of scent receptors
Dogs have more scent receptors, known as olfactory nerves, than cats. Canines have 300 million olfactory receptors on average, while cats only have 200 million.
However, felines are better when it comes to identifying which scents are similar to each other. The reason is the number of V1R receptors found in these animals.
Notably, dogs have 9 V1R scent receptors, while cats have 30, making the latter better at distinguishing smells. However, canines have the advantage in detecting small amounts of odorants, and their brains have a much larger area for processing scents.
2. Usage
Dogs and cats are both renowned for their sense of smell. However, there is a difference in terms of how they use their noses.
- Dogs
-
- Detection. Dogs can detect certain things by remembering the smell of them. For instance, police forces use trained dogs to detect missing persons by making them smell those people’s personal belongings.
- Tracking. A dog’s sense of smell is so strong that it can follow a scent trail for around 12 miles. Considering their sense of smell in distance reached, they make exceptional trackers for hunting and law enforcement or search and rescue operations.
- Medical Detection. With proper training, dogs can be smart enough to detect various medical conditions, such as seizures, cancers, and diabetes. Dogs can detect these illnesses through the changes in a person’s body.
- Emotional Detection. Dogs can sense human emotions through their scent, allowing them to react as if trying to console their caretakers.
- Cats
-
- Territory Marking. Cats use their smell for marking their territory. Then, they use their sense of smell to communicate with other cats.
- Hunting. Felines use their keen noses to locate prey whenever they hunt. Their exceptional scent receptors are particularly beneficial in dark environments where their vision is compromised.
- Identification. Cats use their noses to recognize familiar scents, such as their living environment and caretaker. This way, they can easily find their way back home whenever they wander around the neighborhood.
However, you won’t see police or service cats because dogs are more receptive to training and also have a keen sense of smell, making it more practical to use them.
Which Animal Has a Better Sense of Smell?
While both furry animals have fantastic scent receptors, dogs generally have a better sense of smell than cats. The reason is that, as mentioned, canines have a hundred million more olfactory receptors than cats.
However, felines will have the advantage when it comes to differentiating similar odors, so it all depends on what you consider to be “better.”
Cat Senses vs Dog Senses
Apart from their sense of smell, let us also compare the other four senses in cats and dogs:
1. Sight
Dogs see relatively well in low-light environments. They also possess good motion detection.
However, the accuracy of their color vision is not as good as that of felines.
Felines have fantastic night vision, as they possess more rod cells in their retinas than dogs. However, dogs can see in 240 degrees while cats are limited to 200 degrees.
2. Hearing
Dogs and cats have a highly developed sense of hearing. Dogs are better at detecting low-frequency noise outside of the human range, but both animals are adept at recognizing high-frequency, high-pitch sounds.
Notably, dogs and cats can adjust their ears for better sound locating.
3. Touch
Both dogs and cats have highly sensitive whiskers, which provide them with a keen sense of touch. Their paws are also sensitive, making them useful for detecting texture, vibration, and navigating environments.
Moreover, dogs and cats use their whiskers to detect movements and transmit those movements into their sensory cells. However, dogs often have more whiskers than felines (20 vs. 12 on each side).
4. Taste
Cats have fewer taste buds than dogs. For this reason, the latter can distinguish certain tastes, such as salty, sweet, sour, and bitter better.
On the other hand, the limited number of taste buds in cats makes them unable to taste sweetness.
Conclusion
To sum up our comparison about dog vs cat sense of smell, both dogs and cats rely on their noses to understand their environment. However, it is worth noting that dogs are better scent detectors than cats.
This is the reason why law enforcement usually uses canines to aid them in finding missing people, drugs, bombs, and the like.
Similarly, cats use their sense of smell combined with their exceptional vision and hearing to detect things.

I am Amy Sawy, a Doctor of Veterinary Medicine (DVM) graduate from the University of Kansas. y husband, Dr. Plummer, and I own a veterinary clinic in Phillipsburg, Kansas. In addition to my professional background, I am a devoted pet owner myself, with a household that includes dogs, rodents, and most notably, cats – a total of five felines in my home.
In 2020, I joined an organization as a professional writer, leveraging my experience and collaborating with my team to deliver the most valuable information for your cat’s care.